The Z-Wave Alliance, the standards development organization dedicated to advancing the smart home and Z-Wave technology, has completed the Z-Wave Source Code project. The project opens development of Z-Wave and enables members to contribute code to shape the future of the protocol under the supervision of the new OS Work Group (OSWG).
Z-Wave Source Code is available on GitHub to Z-Wave Alliance members.
Related: eBook Series Offers Guide to Z-Wave Technology Options
The goal of the project is to provide a rich development environment that contains the relevant source code and sample applications to those seeking to play a direct role in the advancement of the Z-Wave standard. The quality and interoperability of products utilizing Z-Wave Source Code will also be enforced by a new mandatory Silicon & Stack Certification program.
Full Z-Wave certification will continue to test and certify for Z-Wave S2 security, network connectivity, range, battery life, and interoperability including backwards and forwards compatibility.
“The Z-Wave Alliance is deeply committed to the global smart home market,” said Mitch Klein, executive director of the Z-Wave Alliance. “This year the smart home conversations have focused largely on Matter. Shiny and new, and with big brands supporting the initiative, Matter is bringing a lot of attention to the smart home. This makes it easy to overlook Z-Wave as the most established, trusted, and secure smart home protocol, that also happens to have the largest certified interoperable ecosystem in the market. We firmly expect that Z-Wave will play a key role in connecting devices and delivering the experience users really want.”
As the Alliance worked to complete the Source Code project, Z-Wave experienced growth, achieving milestones such as the availability of Z-Wave Long Range (LR) certification, surpassing 4100 certified Z-Wave devices in the market, and seeing 90 million new Z-Wave devices enter the market since 2020.
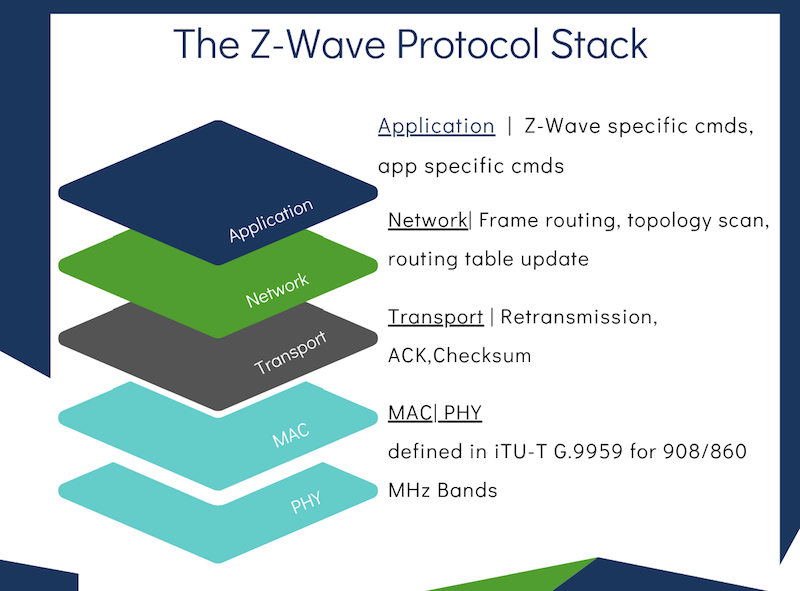
In 2020, when Z-Wave Alliance announced that Silicon Labs was contributing the Z-Wave code to the organization, the Alliance was re-incorporated as an independently run, member-driven non-profit SDO. Over the past 20 months, technical working groups specific to features such as the physical layer working group (mac/PHY), networking layer working group, application layer working group (command class specification), and security working group have collaborated to complete the Z-Wave Source Code project.
Executed in beta testing and shared with members at the Z-Wave Member Summit, Exegin Technologies completed the porting of Z-Wave Source Code to third-party silicon. The operation is outlined in a blog on the Z-Wave Alliance website. The proof-of-concept network demonstrates how the Z-Wave Source Code package will provide developers and manufacturers with flexible implementations from controller (hub/bridge) to end devices. Further extrapolated, the implementation could be for both new controllers, such as Z-Wave/Matter compatible bridges, and for Z-Wave or Z-Wave/Matter end devices.
Silicon Labs, one of the primary code contributors to both Matter and Z-Wave, has developed a multi-protocol software development kit, the Unify SDK, for Matter-based hubs and bridges. The software tool provides for interoperability between the different wireless IoT protocols, including Z-Wave and Matter. The Unify SDK offers a how-to kit for manufacturers and developers to connect both new and legacy Z-Wave devices with new Matter devices.
“This is going to be an incredible year for the smart home industry and an exciting time for verticals we see growing including MDU, hospitality, energy, and insurance,” Klein added. “As an SDO, membership is the key to the future of Z-Wave technology. With a new BoD led by Amazon’s Jonathan Adams and John Osborne II who chaired Project CHIP, the industry will start to recognize and embrace all the shiny parts of Z-Wave.”